
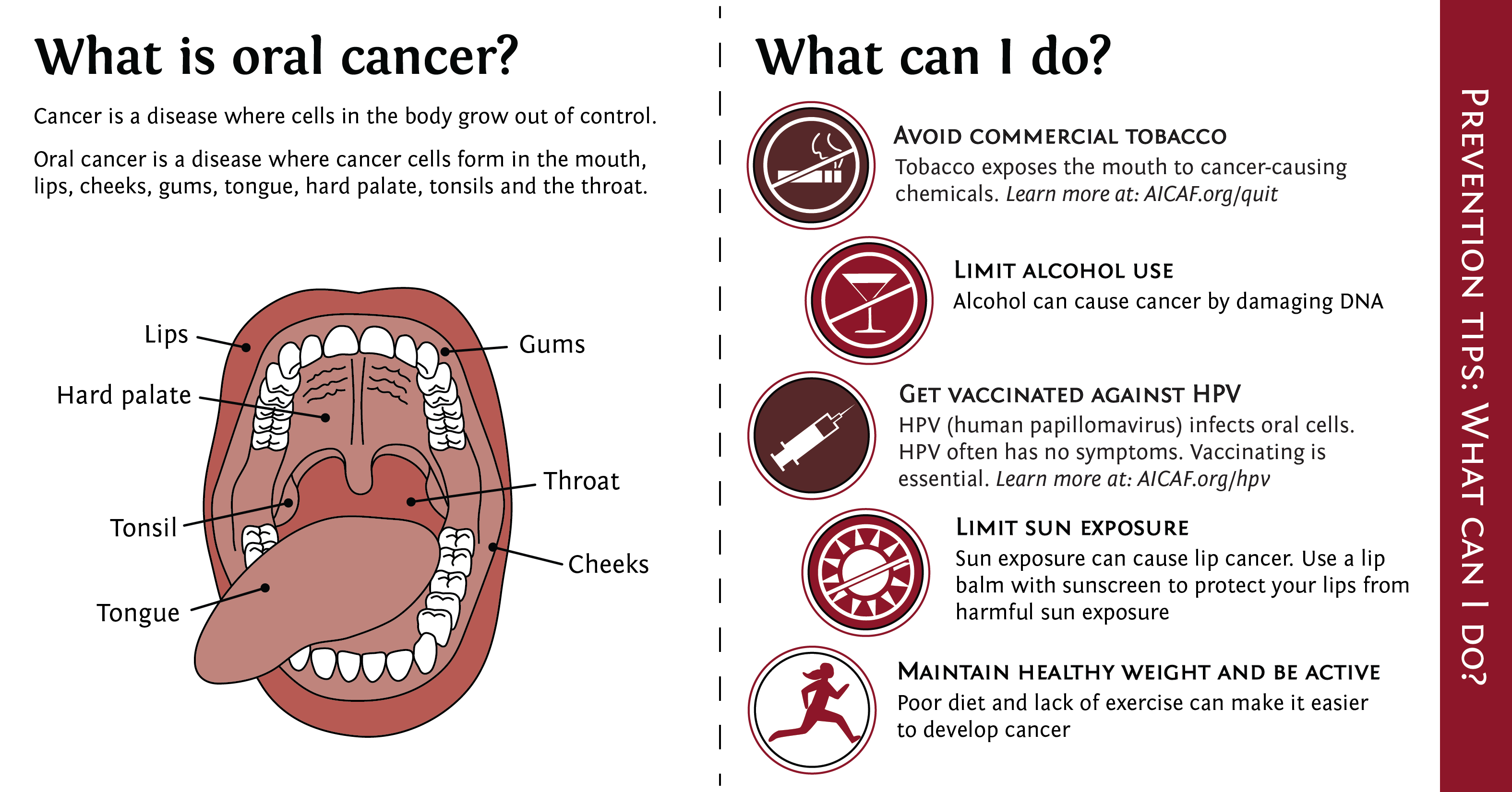
Historically the death rate associated with this cancer is particularly high not because it is hard to discover or diagnose, but due to the cancer being routinely discovered late in its development. Brain cancer, auditory and ocular cancers, and thyroid cancer, (an endocrine system cancer) are cancer categories of their own, and are not included in the head and neck cancer group as identified by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Oral cancers are part of a group of cancers commonly referred to as head and neck cancers, and of all head and neck cancers, they comprise about 85% of that category.
PARANOID ABOUT ORAL CANCER PROFESSIONAL
Data collection and reporting in some countries is problematic in spite of the professional efforts of the WHO to be accurate. Note that the world incidence numbers from the WHO, while the best available, are estimates that users should consider with caveats. Worldwide the problem is much greater, with over 450,000 new cases being found each year. If you expand the definition of oral and oropharyngeal cancers to include cancer of the larynx, the numbers of diagnosed cases grow to approximately 54,000 individuals and 13,500 deaths per year in the U.S. So a change in the etiology, not improved early discovery or treatments which are relatively unchanged from a decade ago, are not the primary cause for improvement.) The death rate for oral cancer is higher than that of cancers which we hear about routinely such as cervical cancer, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, laryngeal cancer, cancer of the testes, and many others. However this is due to the increase of HPV16 caused cancers which are more vulnerable to existing treatment modalities, conferring a significant survival advantage. (The survival number at 5 years from diagnosis was for many decades about 50%, so 57% is an improvement over the last ten years. (Approximately 57%) This is a number that has not significantly improved in decades. Of those 54,000 newly diagnosed individuals, only slightly more than half will be alive in 5 years. It will cause over 9,750 deaths, killing roughly 1 person per hour, 24 hours per day. Accessed March 14, 2020.Close to 54,000 Americans will be diagnosed with oral or oropharyngeal cancer this year. Salivary gland tumors: Epidemiology, diagnosis, evaluation, and staging. Salivary gland cancer treatment (Adult) (PDQ) - Patient version.Cummings Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery. Jobs associated with salivary gland tumors include those involved in rubber manufacturing, asbestos mining and plumbing. People who work with certain substances may have an increased risk of salivary gland tumors. Workplace exposure to certain substances.Radiation treatments for cancer, such as radiation used to treat head and neck cancers, may increase the risk of salivary gland tumors. Though salivary gland tumors can occur at any age, they most commonly occur in older adults. Types of cancerous (malignant) salivary gland tumors include:įactors that may increase your risk of salivary gland tumors include: Types of noncancerous (benign) salivary gland tumors include: Knowing the type of salivary gland tumor you have helps your doctor determine which treatment options are best for you. Doctors classify salivary gland tumors based on the type of cells involved in the tumors. Many different types of salivary gland tumors exist. They can also break away from the tumor and spread (metastasize) to distant areas of the body. Cancer cells can invade and destroy nearby tissue. If additional changes happen in the DNA, the abnormal cells may become cancerous. The abnormal cells go on living when healthy cells would die. The changes tell the cells to grow and divide rapidly. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. Salivary gland tumors begin when some cells in a salivary gland develop changes (mutations) in their DNA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
